Fuel, Oil and Coolant Specifications
ENGINE COOLANT
Engine coolant is considered as any solution which is circulated through the engine to provide the means for heat transfer
from the different engine components. In general, water containing various materials in solution is used for this purpose.
The function of the coolant is basic to the design and to the successful operation of the engine. Therefore, coolant must
be carefully selected and properly maintained.
CORROSION INHIBITORS
COOLANT REQUIREMENTS
A corrosive inhibitor is a water soluble chemical compound
A suitable coolant solution must meet the following basic
which protects the metallic surfaces of the cooling system
requirements:
against corrosive attack. Some of the more commonly
I. Provide for adequate heat transfer.
used corrosion inhibitors are chromates, borates, nitrates,
2. Provide a corrosion resistant environment within the
nitrites and soluble oil.
cooling system.
3. Prevent formation of scale or sludge deposits in the
cooling system.
4. Be compatible with the cooling system hose and seal
materials.
5. Provide adequate freeze protection during cold
weather operation.
The first four requirements are satisfied by combining a
suitable water with reliable inhibitors. When operating
conditions dictate the need for freeze protection, a solution
of suitable water and a permanent antifreeze containing
adequate inhibitors will provide a satisfactory coolant.
WATER
Any water, whether of drinking quality or not, will produce a
corrosive environment in the cooling system. Also, scale
deposits may form on the internal surfaces of the cooling
system due to the mineral content of the water. Therefore,
water selected as a coolant must be properly treated with
inhibitors to control corrosion and scale deposition. To
determine if a particular water is suitable for use as a
coolant
when
properly
inhibited,
the
following
characteristics must be considered: the concentration of
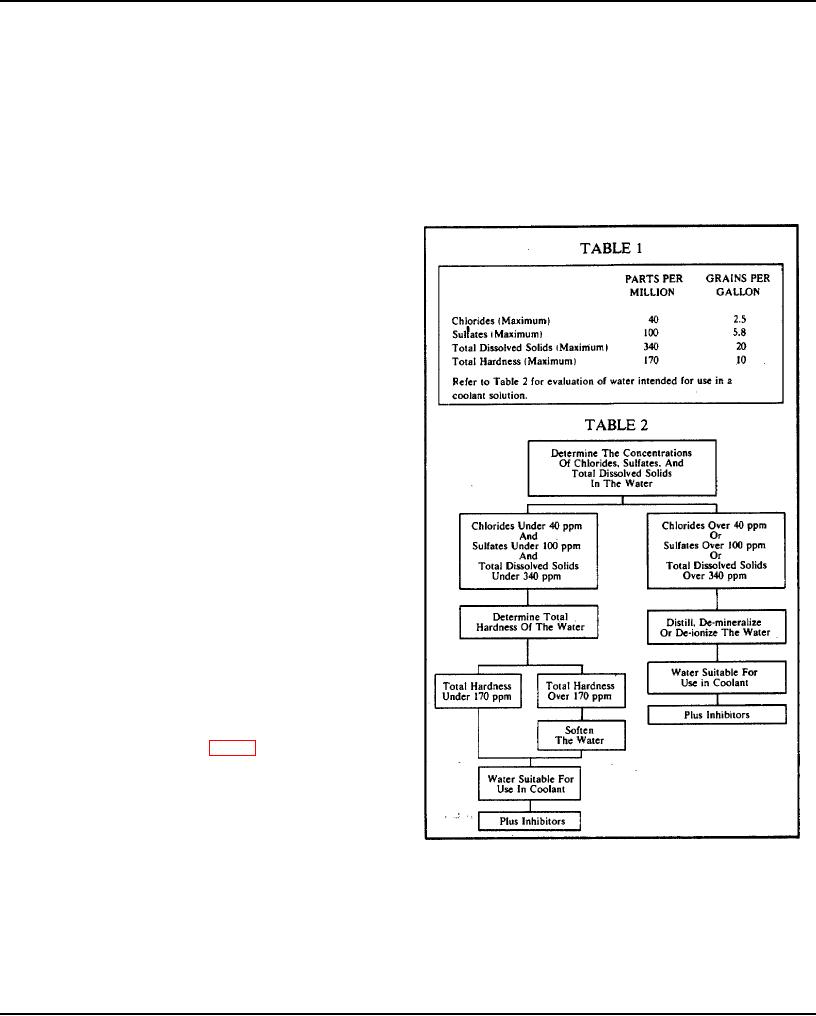
Chlorides and/or sulfates tend to accelerate corrosion,
while hardness (percentage of magnesium and calcium
present) causes deposits of scale. Total dissolved solids
may cause scale deposits, sludge deposits, corrosion or a
combination of these. Chlorides, sulfates, magnesium and
calcium are among but not necessarily all the materials
which make up dissolved solids. Water, within the limits
specified in Tables 1 and 2 of Fig. 1, is satisfactory as an
engine coolant when proper inhibitors are added.
Fig 1. Water Characteristics
Page 71

