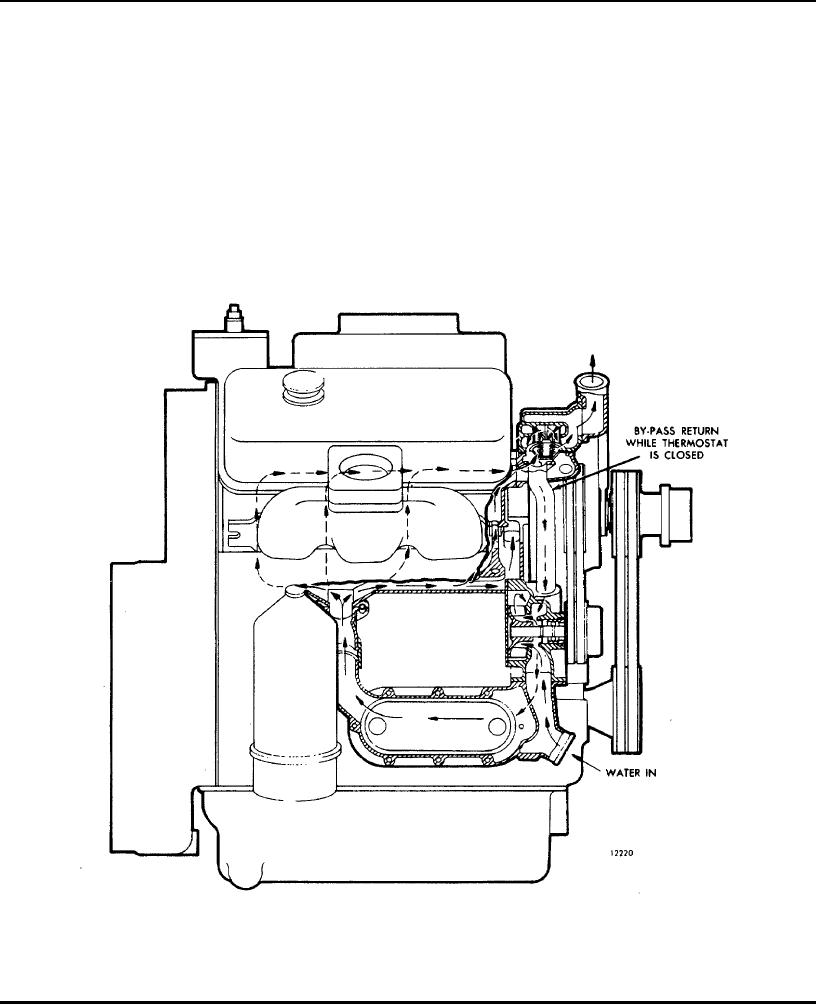
Engine Systems
or by-passes the heat exchanger and flows directly to the water pump, depending on the coolant temperature.
While passing through the core of the heat exchanger, the coolant temperature is lowered by raw water, which is drawn
by the raw water pump from an outside supply. The raw water enters the heat exchanger at one side and' is discharged
at the opposite side.
To protect the heat exchanger element from electrolytic action, a zinc electrode is located in both the heat exchanger
inlet elbow and the raw water pump inlet elbow and extends into the raw water passage.
The length of time a heat exchanger will function satisfactorily before cleaning will be governed by the kind of coolant
used in the engine and the kind of raw water used. Soft water plus a rust inhibitor or a high boiling point type antifreeze
should be used as the engine coolant.
When foreign deposits accumulate in the heat exchanger to the extent that cooling efficiency is impaired, such deposits
can, in most instances, be removed by circulating a flushing compound through the fresh water circulating system without
removing the heat exchanger. If this treatment does not restore the engine's normal cooling characteristics, contact an
authorized Detroit Diesel Allison Service Outlet.
Fig. 19 - Typical Cooling System for V-Type Engine
Page 26

